How To Reduce Your Ecological Footprint: Practical Tips For A Sustainable Lifestyle
Discover how plant-based detoxification helps cleanse the body, improve digestion, boost energy and promote mental well-being. Practical tips, recipes and myths debunked!
Introduction: What is the ecological footprint and why is it important to reduce it?
Today, when we are increasingly confronted with terms such as climate change, biodiversity loss and pollution, it is important to think about how our daily activities affect the planet. One of the key concepts that helps us understand our impact on the environment is the ecological footprint.
What is the ecological footprint?
Ecological footprint is a measure of how much natural resources we consume and the impact our lifestyle has on the planet.
It includes everything from the energy we use, to the food we consume, to the waste we produce.
Simply put, the ecological footprint shows how much land and water is needed to support our way of life.Unfortunately, most of us live in ways that exceed the capacity of the planet.
According to statistics, we would need more than one Earth to sustain our current levels of consumption and production.
This leads to depletion of natural resources, air and water pollution, and other environmental problems that threaten the future of us all.
Why is it important to reduce our ecological footprint?
Reducing our ecological footprint is not just about protecting nature - it's also about securing a better future for ourselves and future generations. Climate change, one of the biggest challenges of our time, is closely linked to our way of life.
Excessive greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation and pollution have devastating impacts on ecosystems, animals and human communities.
Biodiversity loss is another alarming problem. Thousands of plant and animal species disappear every year, upsetting the balance of nature. Pollution, whether it is plastics in the oceans or chemicals in the soil, threatens not only nature but also our health.
By reducing our ecological footprint, we can:
> Contribute to the conservation of natural resources.
> To mitigate the impacts of climate change.
> Promote a healthier and more sustainable environment.
> Ensure a better quality of life for future generations.
Key areas where we can influence our ecological footprint
The good news is that each of us can make a difference. There are many areas where we can reduce our ecological footprint.
Some of the most important ones include:
- 1. Diet and nutrition: Switching to a plant-based diet, minimising food waste and promoting local and seasonal food.
- 2. Energy and household: Energy conservation, switching to renewable sources and water efficiency.
- 3. Transport: Reducing transport emissions, promoting public transport and switching to greener alternatives.
- 4. Consumption and shopping: Minimalism, promotion of sustainable brands and second-hand shopping.
- 5. Waste and recycling: Zero waste, proper waste sorting and reduction of single-use plastics.
Motivation for action: Every step counts
You may feel that as individuals you can't make much of a difference. But the truth is that even small changes can have a huge impact if enough people embrace them. Every step, whether it's reducing plastic, switching to a plant-based diet or saving energy, counts.
This article will offer practical tips and advice on how to get started. It's not about changing everything at once, but about taking incremental steps that will bring you closer to a more sustainable lifestyle. Remember that each of us has the power to influence the future of our planet. Start today - the planet will thank you!
Diet and nutrition: How to influence your ecological footprint through food
Food is one of the most important areas where we can reduce our ecological footprint. What we eat has a direct impact on the environment, and changing our eating habits can be one of the most effective ways to help protect the planet. In this section we focus on three key areas: switching to a plant-based diet, promoting local and seasonal food, and minimising food waste.
Switching to a plant-based diet
Environmental impact of livestock production
Livestock production is one of the biggest contributors to climate change. Meat and dairy production is associated with high emissions of greenhouse gases, in particular carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O).
For example, cattle farming produces huge amounts of methane, which is up to 25 times more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than CO2.
Another problem is water consumption. It takes approximately 15 000 litres of water to produce one kilogram of beef, whereas it takes only 290 litres to produce one kilogram of potatoes.
In addition, livestock production contributes to deforestation, as large areas of rainforest are cleared to make way for grazing land or to grow fodder for livestock.
The benefits of a plant-based diet for the planet and health
Switching to a plant-based diet has many benefits. Ecologically, it reduces greenhouse gas emissions, saves water and helps protect natural ecosystems.
A plant-based diet also promotes biodiversity by reducing pressure on farmland and allowing habitats to recover.
The health benefits of a plant-based diet are also significant. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds is associated with a lower risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity and some cancers.
In addition, it contains more fiber, vitamins and antioxidants that promote overall health.
Practical tips: How to start veganism or reduce meat consumption
> Meatless Monday: Start by skipping meat one day a week. This simple step will help you discover new plant-based recipes and gradually get used to the change.
> Experiment with plant-based alternatives: Try plant-based meat substitutes such as tofu, tempeh, seitan or legumes.
> Gradual changes: You don't have to go vegan overnight. Start by cutting back on red meat and gradually add more plant-based foods to your diet.
> Inspiration from cookbooks and blogs: There are many sources that offer tasty and simple vegan recipes.
Local and seasonal food
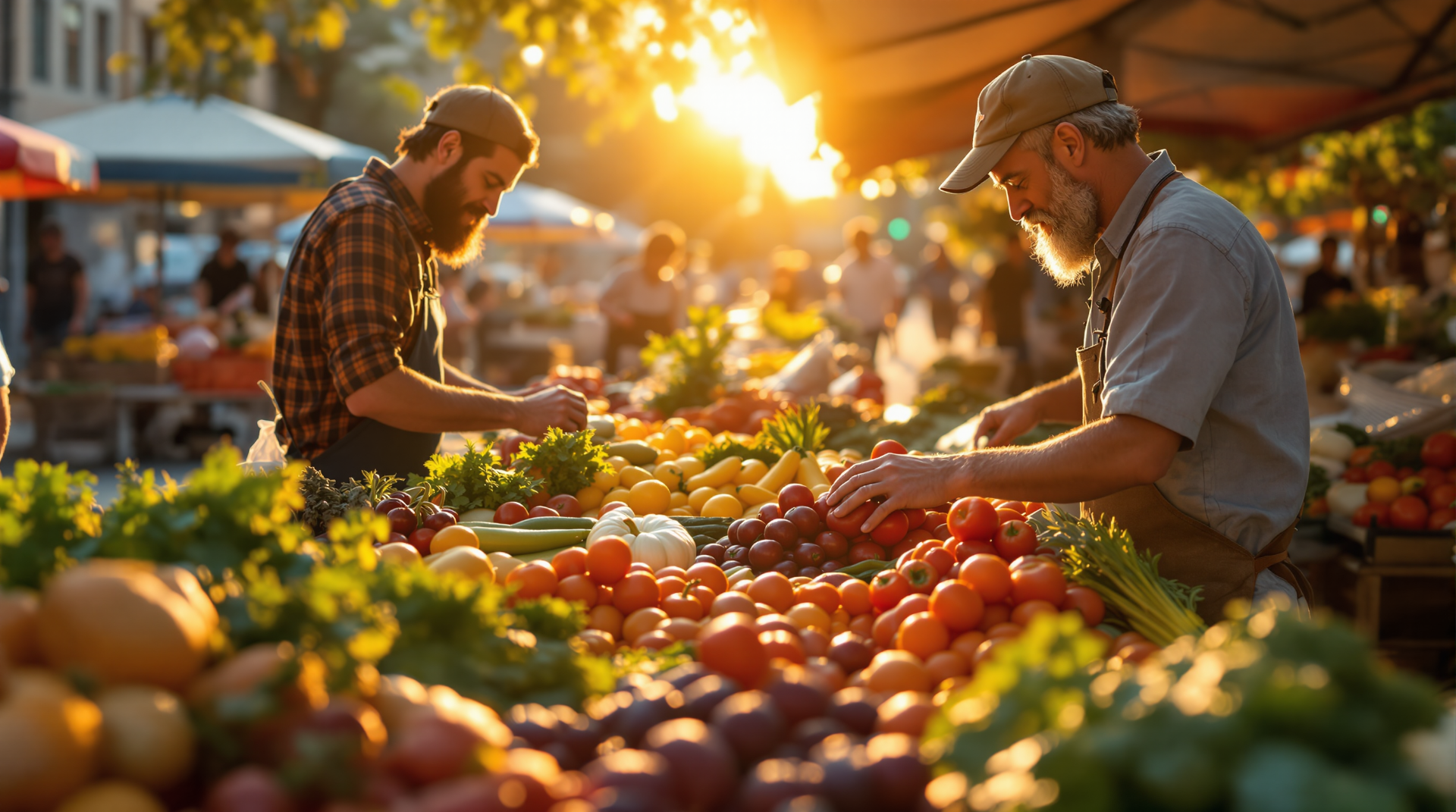

Why it's important to support local farmers and eat seasonal produce
Supporting local and seasonal food has many benefits. Local food has a smaller carbon footprint because it does not require long transport journeys that are often associated with CO2 emissions.
In addition, by buying from local farmers you are supporting the local economy and helping to maintain traditional farming practices.
Seasonal food is not only greener, but also tastier and more nutritious. Fruits and vegetables that are harvested in their natural season taste better and contain more nutrients than produce that is grown in greenhouses or imported from distant lands.

How to find farmers' markets or community gardens
Farmers' markets: find farmers' markets in your area where you can buy fresh and seasonal food directly from farmers.
Community gardens: Join a community garden where you can grow your own fruit and vegetables. This activity will not only provide you with fresh food, but also connect you with nature and the community.
Support Local Farmers: Consider joining Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) programs where you can subscribe to a share of a local farm's harvest.
Minimising food waste
Statistics on food waste
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced each year is wasted, equivalent to about 1.3 billion tonnes. This waste has a huge impact on the environment because wasting food also means wasting resources such as water, energy and land.
Tips on food storage, menu planning and using leftovers
> Menu planning: Create a weekly meal plan and buy only what you really need.
> Correct storage: Learn how to store food properly so it lasts longer. For example, keep vegetables in the fridge in perforated bags and fruits separate from vegetables.
> Use leftovers: You can use leftovers creatively - for example, use leftover vegetables in soups or sauces.
> Composting: If you still produce food waste, consider composting to return nutrients back to the soil.
Changes in eating habits can have a huge impact on our ecological footprint. Switching to a plant-based diet, promoting local and seasonal food and minimising food waste are steps that not only help the planet, but also improve our health and quality of life. Start with small steps and gradually discover new ways to contribute to a more sustainable future.
Energy and home: How to reduce the ecological footprint of your home
The home is one of the places where we can make the biggest changes to reduce our ecological footprint. Energy and water consumption has a direct impact on the environment, so it is important to focus on resource efficiency. In this section we look at practical tips on how to save energy, switch to renewable sources and manage water better.
Saving energy in the home
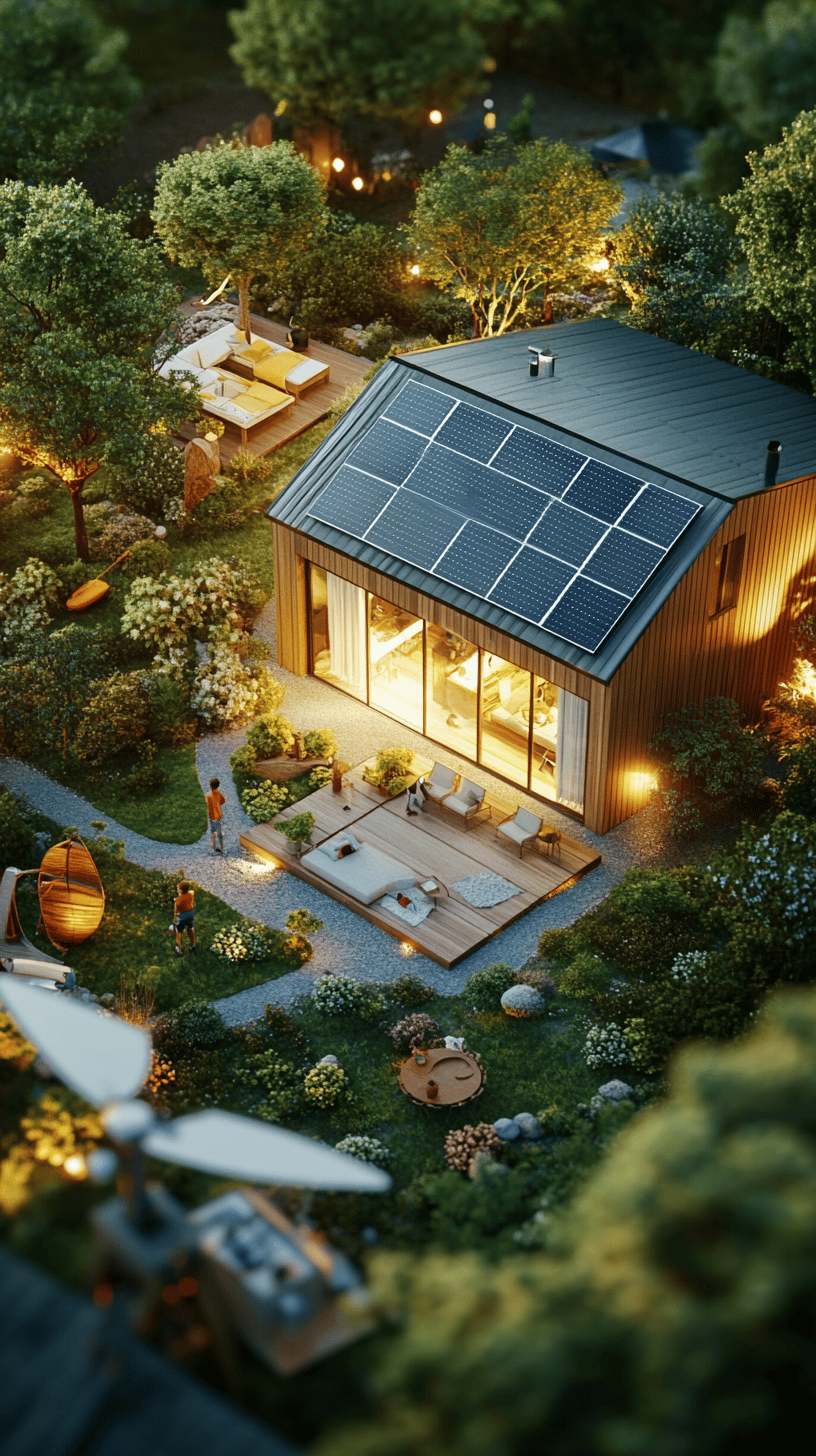
How to reduce energy consumption
Household energy consumption is a significant part of our environmental footprint.
Fortunately, there are many simple ways to reduce it:
> LED light bulbs: Replacing conventional light bulbs with LED bulbs is one of the easiest steps to save energy. LED bulbs use up to 80% less energy and last longer.
> Switching off appliances: Appliances in stand-by mode still consume energy. Turn them off completely, or use extension cords with a switch that make it easy to unplug multiple devices at once.
> Energy-saving appliances: When buying new appliances, choose those with high energy efficiency (labelled A++ or A+++). These appliances use less energy and save money in the long run.

The importance of home insulation and efficient heating
Properly insulating your home or apartment is key to reducing your heating and cooling energy consumption.
> Insulation: Insulation of walls, roof and windows can significantly reduce heat loss. Investing in quality insulation will quickly pay for itself in lower energy bills.
> Efficient heating: Use thermostats and set the temperature to the optimum level (e.g. 20-22 °C during the day and 18 °C at night). Regularly maintain heating systems to keep them working as efficiently as possible.
> Ventilation: Instead of long periods of ventilation with open windows, try short and intensive ventilation to minimise heat loss.
The importance of home insulation and efficient heating
Properly insulating your home or apartment is key to reducing your heating and cooling energy consumption.
> Insulation: Insulation of walls, roof and windows can significantly reduce heat loss. Investing in quality insulation will quickly pay for itself in lower energy bills.
> Efficient heating: Use thermostats and set the temperature to the optimum level (e.g. 20-22 °C during the day and 18 °C at night). Regularly maintain heating systems to keep them working as efficiently as possible.
> Ventilation: Instead of long periods of ventilation with open windows, try short and intensive ventilation to minimise heat loss.
Renewable energy sources

Switching to green energy
Renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind power are the key to a more sustainable future.
Switching to green energy not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes the development of clean technologies.
- Solar panels: Installing solar panels on your roof allows you to generate your own electricity and reduce your dependence on fossil fuels. You can even sell excess energy back to the grid.
- Wind power: If you live in an area with sufficient wind, you might consider installing a small wind turbine.

How to choose a renewable energy supplier
If you don't have the option to install your own renewable energy, you can switch to a supplier that offers renewable energy.
- Compare offers: Look for suppliers who guarantee that their energy comes from renewable sources such as solar, wind or hydroelectric.
- Certification: Look for certifications that confirm that the supplier is actually using renewable resources (e.g. Green Energy Certificate).
- Support community projects: Some suppliers support local renewable energy projects, which can be another way to contribute to sustainability.
How to choose a renewable energy supplier
If you don't have the option to install your own renewable energy, you can switch to a supplier that offers renewable energy.
- Compare offers: Look for suppliers who guarantee that their energy comes from renewable sources such as solar, wind or hydroelectric.
- Certification: Look for certifications that confirm that the supplier is actually using renewable resources (e.g. Green Energy Certificate).
- Support community projects: Some suppliers support local renewable energy projects, which can be another way to contribute to sustainability.
Water as a valuable resource
Tips for saving water
Water is one of nature's most precious resources, yet we often waste it. Here are some tips on how to reduce water consumption in the home:
> Perlators: Installing perlators on taps and showers can reduce water consumption by up to 50% without affecting comfort.
> Rainwater harvesting: You can use rainwater to water your garden, wash your car or flush your toilet.
> Shorter showers: Reduce the shower time to 5 minutes and turn off the water when soaping or shampooing.
The environmental impact of wasting water
Wasting water has not only economic but also environmental consequences. Pumping and treating water requires energy, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, excessive use of water resources can lead to their depletion and threaten the ecosystems that depend on them.
Changes in energy and water management can have a huge impact on our ecological footprint. Saving energy, switching to renewable sources and using water sparingly are steps that not only help the planet, but also reduce the cost of running a household. Start with small changes and gradually move on to bigger measures - every step counts!
Transport: How to reduce your ecological footprint when travelling
Transport is one of the biggest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, so it is crucial to focus on ways to reduce its environmental impact. Whether it's daily commuting, longer journeys or holidays, there are many ways to travel more sustainably. In this section we look at the benefits of public transport, electric mobility and alternative fuels, and how to reduce air travel.
Reducing emissions from transport
Benefits of public transport, cycling and walking
One of the easiest ways to reduce your ecological footprint is to reduce the use of cars. Public transport, such as buses, trains or trams, is much more efficient in terms of emissions per person.
For example, train transport produces up to 80% less CO2 emissions per kilometre than driving.
Cycling and walking are not only environmentally friendly but also healthy. Cycling or walking helps improve physical fitness, reduces stress and produces no emissions.
For shorter distances, these modes of transport are an ideal alternative to the car.
Shared transport and carpooling as an efficient solution
If car use is necessary, carpooling is a great way to reduce emissions. By sharing rides with others, you can reduce the number of cars on the road, leading to lower emissions and less congestion. There are also platforms and apps that make it easier to organise ridesharing.
Electromobility and alternative fuels
Switching to electric vehicles and their environmental benefits
Electric vehicles (EVs) represent a significant step towards more sustainable transport. Unlike vehicles with internal combustion engines, they emit no emissions during operation. If they are charged with electricity from renewable sources, their environmental footprint is even lower.
Another advantage of EVs is lower running costs - electricity is usually cheaper than petrol or diesel, and EVs have fewer moving parts, which means lower maintenance costs.
What are the options for alternative fuels (e.g. biogas)
In addition to electric cars, there are other environmentally friendly alternatives such as biogas, hydrogen and hybrid vehicles.
Biogas: Vehicles powered by biogas use gas produced from organic waste, which reduces emissions while encouraging recycling.
Hydrogen: Hydrogen cars produce only water vapour as a by-product, which is ideal in terms of emissions. However, their wider use is still hampered by a lack of infrastructure.
"Disadvantages of electric cars"
Although electric cars offer many environmental advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
Availability of charging infrastructure: although the network of charging stations is constantly expanding, it may still be insufficient in some areas. This can limit convenience and flexibility for longer journeys.
Charging time: Charging an electric car takes longer than filling up with petrol or diesel. While fast chargers can reduce charging time, it can still be a disadvantage for those who need a quick recharge.
Range: Although the range of electric vehicles is improving, it can still be a limitation for some users, especially on longer journeys without available charging stations.
Ecological footprint of battery production: The production of batteries for electric vehicles is energy intensive and can have a negative impact on the environment, especially when it comes to the extraction of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt and nickel
.Cost: The purchase price of EVs is often higher than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, which can be a barrier for some consumers, although the cost of ownership can be offset by lower operating costs.
Despite these drawbacks, EVs represent an important step towards a more sustainable transport future. As technology and infrastructure continue to advance, these disadvantages are expected to diminish over time.
Air traffic restrictions
Climate impact of air transport
Air transport is one of the largest sources of CO2 emissions per person. A single long-haul flight can produce more emissions than the average person produces in an entire year from other activities.
In addition, aircraft emissions have a greater impact on the climate because they are emitted in the upper atmosphere.
Tips for planning a holiday with a smaller ecological footprint
> Train: For shorter and medium distance travel, trains are a greener alternative to planes. Modern trains are comfortable, fast and produce far fewer emissions.
> Holidays closer to home: Consider exploring local destinations that are accessible by car, train or bus. Traveling around your own country or neighboring states can be just as rewarding as an exotic vacation.
> Emissions Offset: If a flight is unavoidable, consider offsetting emissions through programs that invest in climate protection projects such as planting trees or promoting renewable energy.
Changes in transport habits can have a significant impact on our ecological footprint. Whether it's switching to public transport, ridesharing, using electric cars or reducing air travel, every step towards more sustainable transport counts. Start with small changes and gradually discover new ways to travel green while helping to protect our planet.
Consumption and shopping: How to reduce your ecological footprint through conscious consumption
Our consumption habits have a major impact on the environment. Every purchase we make affects not only our wallet, but also the planet. From the production and transportation of products to their disposal, every step in the product life cycle leaves an ecological footprint. In this section, we'll focus on minimalism, supporting sustainable brands and giving things a second chance.
Minimalism and conscious consumption
How to reduce unnecessary purchases and focus on quality instead of quantity
Minimalism isn't just about owning less stuff, it's about a conscious approach to consumption. Instead of hoarding unnecessary items, focus on quality and functionality.
> Plan your purchases: Make a list before each purchase and stick to it. This will help you avoid impulse purchases.
> Invest in quality: Quality products last longer, which means less waste and lower costs in the long run. For example, quality clothes or electronics last for years, while cheap alternatives wear out quickly.
> Avoid trends: Fashion trends and seasonal sales often tempt us to buy things we don't need. Focus on timeless pieces that will last a long time.
The meaning of the question, "Do I really need this?"
Before making any purchase, ask yourself a simple question: "Do I really need it?" This approach will help you distinguish between real needs and wants.
If the answer is "no," consider whether your money could be better invested, for example, in experiences or savings.
Supporting sustainable brands
How to recognise ethical and eco-friendly brands
Supporting sustainable brands is one of the best ways to reduce your environmental footprint. These brands focus on production that is environmentally friendly and respects workers' rights.
- Transparency: Look for brands that openly share information about their production processes, materials and supply chains.
- Local production: Supporting local producers reduces emissions associated with transportation and supports the local economy.
- Materials: Prefer products made from recycled, organic or renewable materials.
Importance of certifications (e.g. Fair Trade, GOTS)
Certifications are a great guide when choosing sustainable products. Some of the best known include:
- Fair Trade: Guarantees fair working conditions and fair wages for workers in developing countries.
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): A certification for textiles made from organic materials that ensures ecological and ethical production.
- FSC (Forest Stewardship Council): A certification for wood and paper that guarantees that materials come from responsibly managed forests.
A second chance for things
Advantages of buying second hand
Buying second hand is one of the best ways to reduce waste and extend the life cycle of products.
- Second-hand clothing: Buying second-hand clothing reduces the demand for new production, which is often associated with high water and chemical consumption. Plus, you can find unique pieces at a fraction of the price.
- Refurbished electronics: Refurbished phones, computers or other electronic devices are more affordable and environmentally friendly than new products.
How to properly recycle and donate unwanted items
If you have items at home that you no longer need, consider donating or recycling them.
- Donate: You can donate unwanted clothes, furniture or electronics to charities, community centres or friends.
- Recycling: Learn how to sort waste properly and use collection yards for recycling electronics, batteries or other special materials.
- Swap events: Participate in swap events where you can exchange unwanted items for something you can use.
Consumption and shopping are areas where we can make a big difference. Minimalism, supporting sustainable brands and giving things a second chance are steps that not only help the planet, but also encourage a more conscious and meaningful lifestyle. Every purchase is a choice - choose one that benefits not only you, but the future of our planet.
Waste and recycling: How to reduce your ecological footprint by managing waste correctly
Waste is one of the biggest problems in modern society. Every year, millions of tonnes of waste end up in landfills or in the oceans, with a devastating impact on the environment. Yet there are many ways we can reduce and better manage waste. In this section we will focus on the concept of zero waste, proper waste sorting and reducing single-use plastics.

Zero waste as a lifestyle
What is zero waste and how to get started
Zero waste is a lifestyle that aims to minimise the amount of waste we produce. This approach focuses on reusing, recycling and composting to ensure that as little waste as possible goes to landfill or into the environment.
Getting started with zero waste doesn't have to be complicated. The key is to gradually introduce small changes into everyday life:
> Refuse: Refuse things you don't need, such as single-use plastic bags or advertising leaflets.
> Reduce: Reduce the amount of things you buy and focus on quality instead of quantity.
> Reuse: Use reusable products such as cloth bags or glass containers.
> Recycle: Sort waste and recycle everything you can.
> Rot (Compost): Compost organic waste such as food scraps or garden waste.
Practical tips for a zero waste lifestyle
- Cloth bags: Replace plastic bags with reusable cloth bags.
- Reusable bottles and cups: Invest in a good quality water bottle or thermal cup so you don't have to buy drinks in disposable containers.
- Composting: If you have a garden, start a compost heap. You can use a vermicomposter or community composting stations in your home.
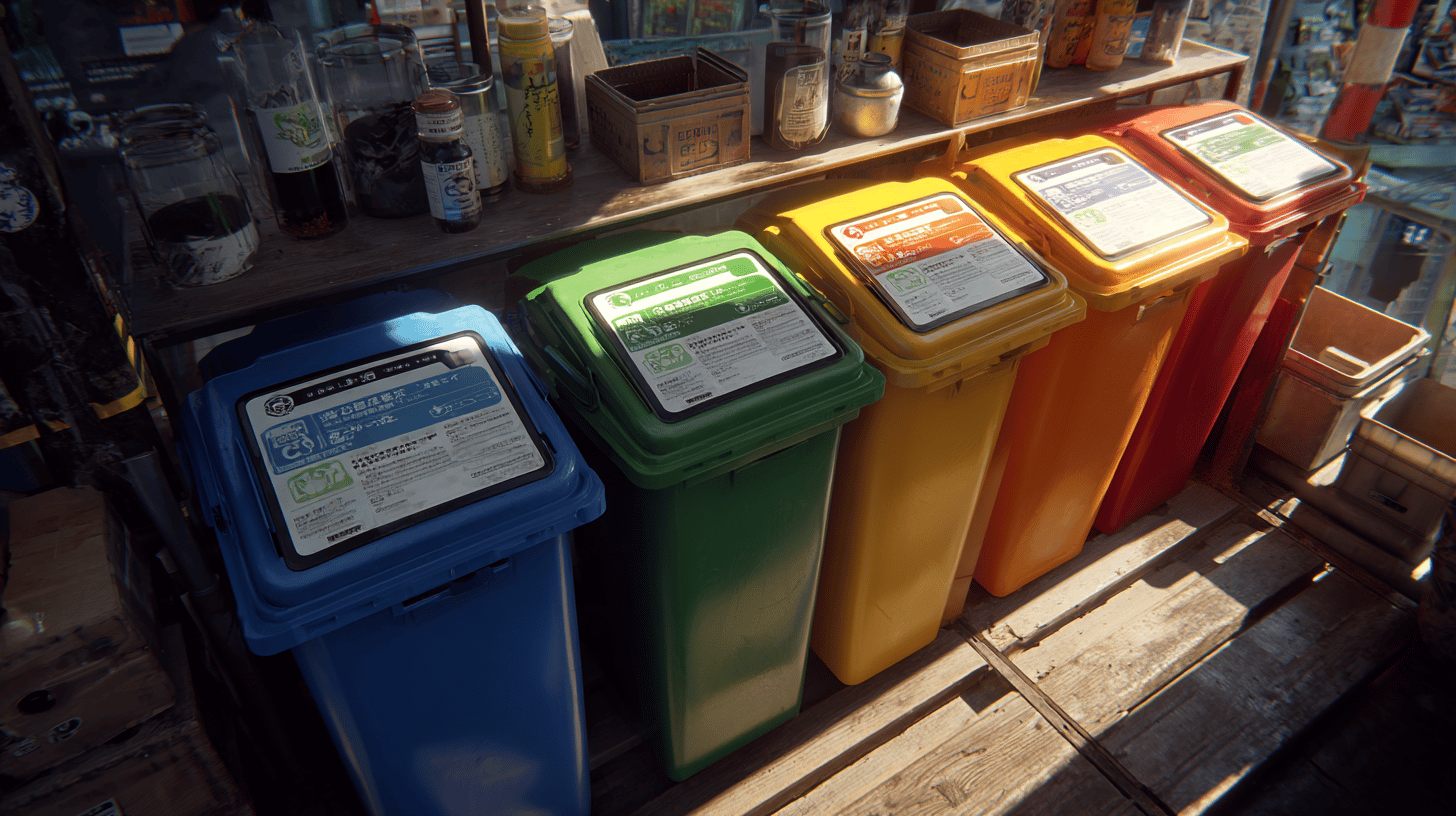
Proper waste sorting
How to sort waste correctly and what can be recycled
Proper waste sorting is the basis for sustainable waste management. Each material has its own specific recycling requirements:
> Paper: Recycle newspapers, magazines, cardboard and office paper. However, avoid greasy or soiled paper.
> Plastics: Sort PET bottles, food packaging and plastic containers. However, do not include mixed plastics or chemical packaging.
> Glass: Recycle glass bottles and containers, but avoid ceramics or mirrors.
> Metals: Sort cans, aluminum foil and metal packaging.
The importance of recycling to reduce the burden on landfills
Recycling helps to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills while saving natural resources.
For example, recycling one tonne of paper saves approximately 17 trees and 26,000 litres of water.
In addition, recycling reduces the greenhouse gas emissions that are created when new materials are produced.

Restrictions on single-use plastics
Alternatives to plastic products
Disposable plastics such as straws, bags or cups are among the biggest polluters of the environment.
However, there are many eco-friendly alternatives:
> Bamboo toothbrushes: Replace plastic toothbrushes with bamboo toothbrushes, which are biodegradable.
> Metal straws: Instead of plastic straws, use metal or glass straws that can be reused.
> Waxed napkins: Replace plastic wrap with waxed napkins, which are reusable and environmentally friendly.
How to avoid plastic packaging when shopping
> Packaging-free shops: Shop at shops that offer food and other products without packaging. Bring your own containers or bags.
> Bring your own packaging: Use cloth bags instead of plastic when buying fruit, vegetables or baked goods.
> Bulk shopping: Buy food in large quantities to reduce packaging.
Reducing and properly managing waste is key to protecting the environment. By adopting zero waste principles, sorting waste and reducing single-use plastics, we can all contribute to a more sustainable future. Remember, even small changes can have a big impact - start today!
Community and social impact: Together for a more sustainable future
Sustainable lifestyles are not just about individual change, but also about collaboration and support within the community. Getting involved in local environmental initiatives, participating in community projects and inspiring others can have a huge impact on our surroundings and the planet. In this session we will look at how to become an active part of change and how we can work together to build a more sustainable world.
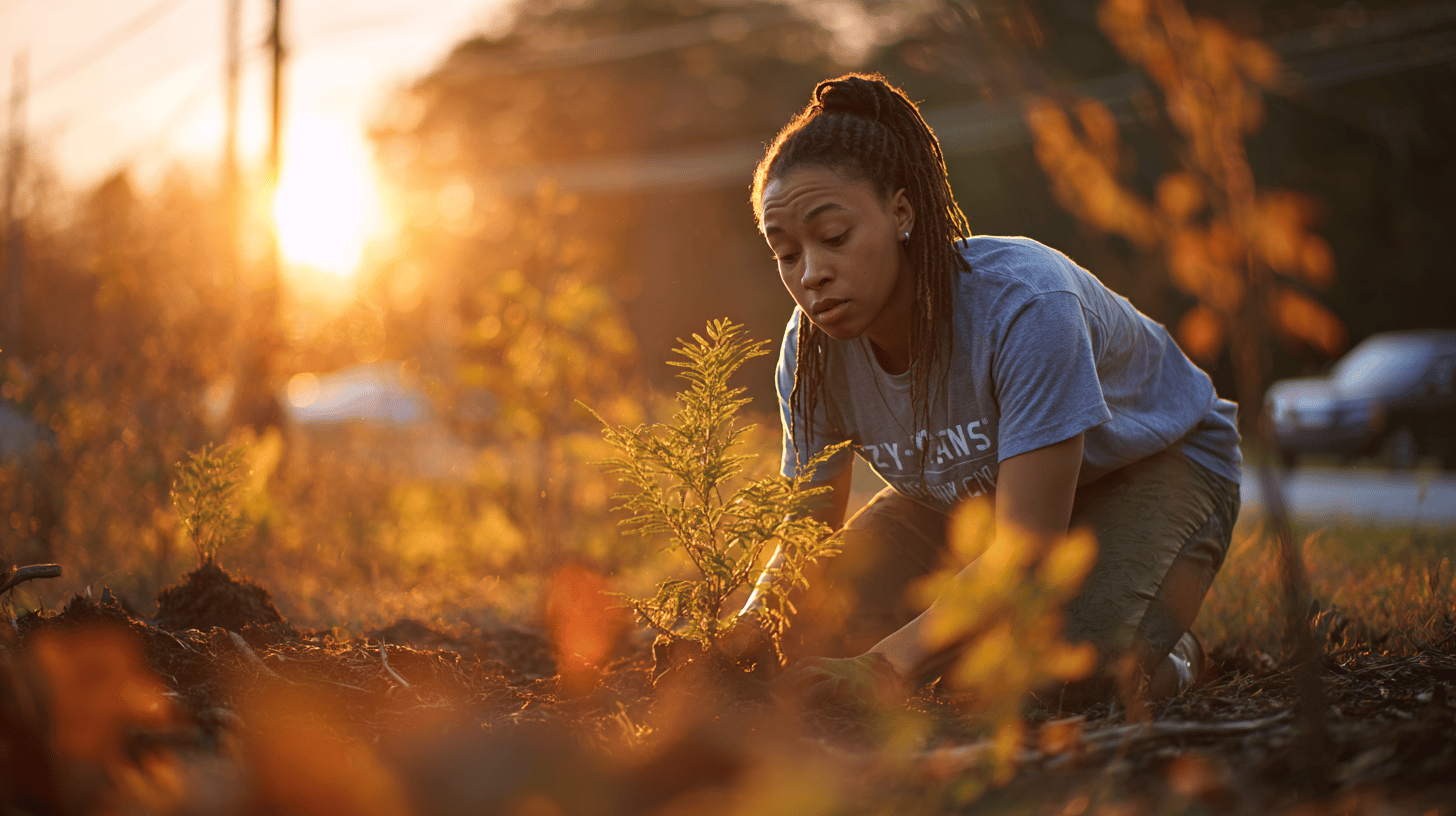
How to get involved in local environmental initiatives
Getting involved in local environmental initiatives is a great way to help protect the environment while connecting with people who share the same values.
- Volunteer: Join local organisations that focus on conservation, public space clean-up or tree planting. These activities not only help nature, but also strengthen community ties.
- Environmental campaigns: Support campaigns to reduce waste, protect biodiversity or promote renewable energy. For example, you can get involved by signing petitions, attending demonstrations or spreading the word on social media.
- Educational events: Attend workshops, lectures or seminars on sustainability and ecology. These events can provide you with new knowledge and inspiration for your next steps.
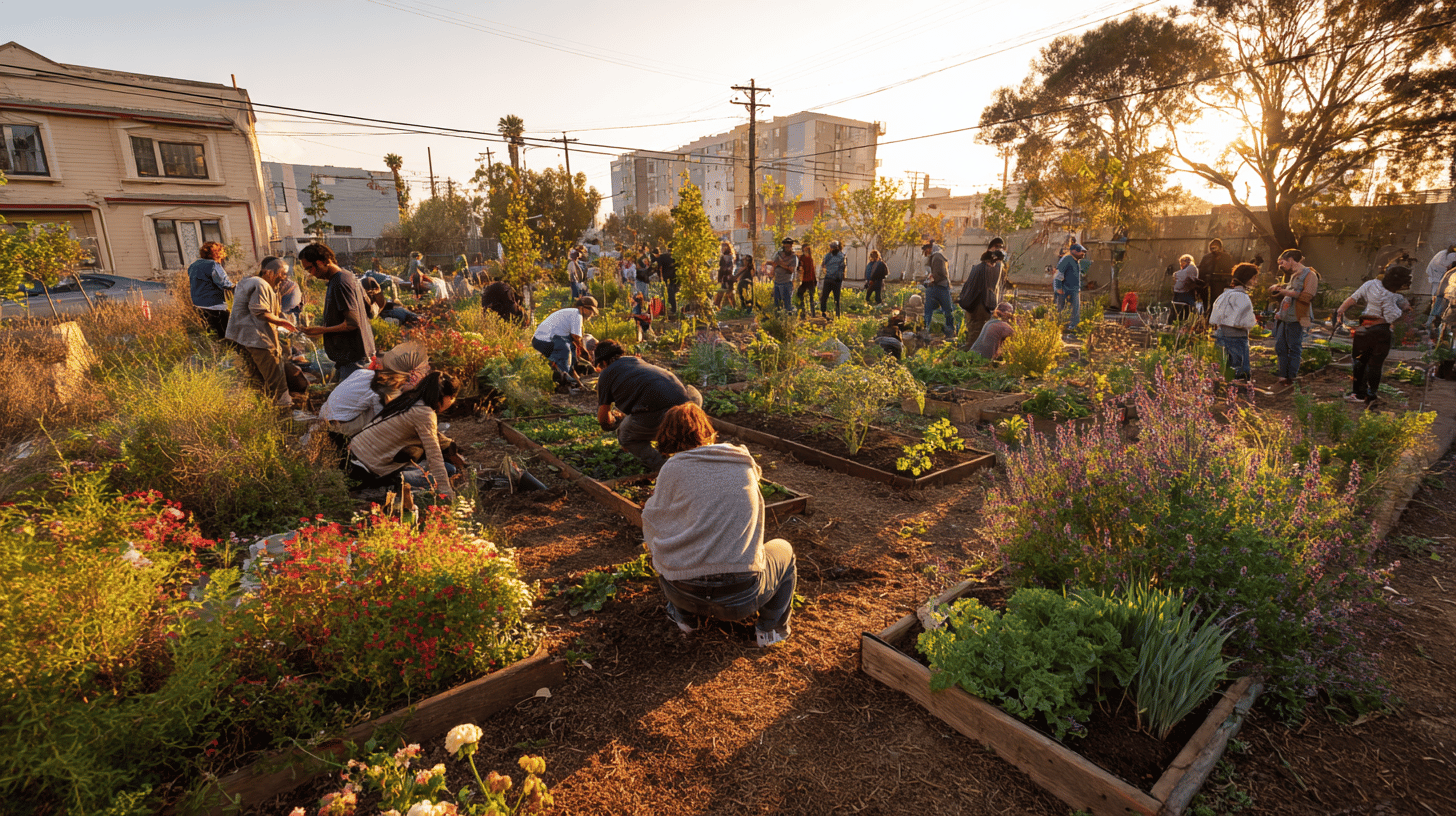

The importance of community gardens, swap events and neighbourhood projects
Community projects are an important tool for building more sustainable and connected communities.
- Community gardens: These gardens provide space to grow your own food, reducing the ecological footprint associated with transporting and packaging food. In addition, they encourage collaboration between neighbours and create opportunities for learning and sharing.
- Swap events: Swap events where people can exchange clothes, books or other items help reduce waste and promote a circular economy. These events are also a great opportunity to meet people who share similar values.
- Neighbourhood projects: Joint activities such as cleaning up public spaces, planting trees or organising neighbourhood markets strengthen community ties and raise awareness of environmental issues.
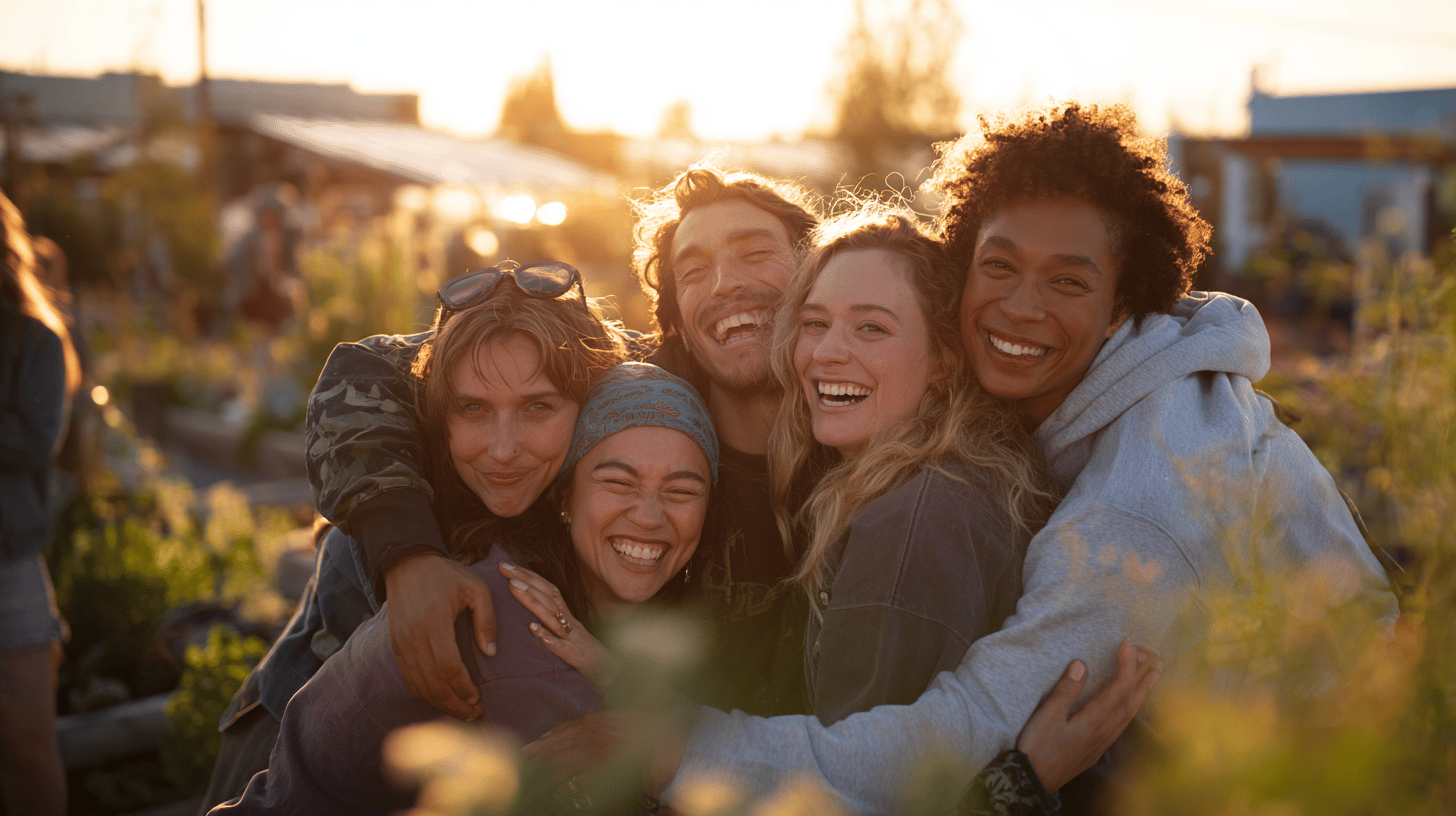

How to inspire others to a sustainable lifestyle
One of the most effective ways to encourage change is to inspire others by your own example.
- Share your experience: Talk about your steps towards a more sustainable lifestyle with family, friends and colleagues. Share tips, recipes or stories that can motivate others.
- Social media: Use social media to spread the word about environmental issues. Share articles, videos or photos that show how small changes can have a big impact.
- Promote education: If you can, organise workshops or lectures on sustainability. Education is the key to long-term change.
- Positive attitude: Instead of criticism, focus on support and motivation. Encourage others to start with small steps and show that a sustainable lifestyle can be easy and rewarding.
Engaging with the community and supporting social change are key to building a more sustainable future. We can all contribute - whether by volunteering, participating in community projects or inspiring others. Together we can create a world that is kinder to nature and fairer for all. Start today and be part of a positive change!
Conclusion: Small steps to big changes
Our journey to a more sustainable lifestyle starts with each of us. In this article we've looked at key areas where we can reduce our environmental footprint - from transport, consumption and shopping, to waste and recycling, to getting involved in community projects. Each of these steps is important and together they can help protect our planet for future generations.
It is important to remember that change does not have to be instant or perfect. Every small step we take counts. It could be swapping a plastic bottle for a reusable one, switching to public transport, getting involved in a local green initiative or just thinking about what we really need. These small steps can gradually become part of our daily lives and inspire others around us. Remember that each of us has the power to influence the future. We don't have to change the whole world at once, just start with ourselves. Whatever change you decide to make, know that even small steps can have a big impact. Call to action - Everyone can make a difference - start today!" Take the first step, no matter how small, and gradually move on to bigger changes. Together, we can create a world that is more environmentally friendly, fairer and more sustainable. The planet will thank us for it.
Bonus:
Practical resources and links for a sustainable lifestyle
If you're interested in sustainability and want to learn more, we've put together a list of useful books, documents, websites and apps to help you on your way to a greener lifestyle. These resources will give you inspiration, practical advice and tools to track your progress.
Recommended books
"Zero Waste" (Bea Johnson): a book by a pioneer of the zero waste lifestyle that offers practical tips on how to minimize waste in everyday life.
"The Future We Choose" (Christiana Figueres and Tom Rivett-Carnac): An inspiring look at the climate crisis and the steps we can take for a sustainable future.
"Food First" (Jonathan Safran Foer): A book that explores the impact of our eating habits on the planet and offers solutions to eat more sustainably.
Recommended documents
"Cowspiracy": a documentary about the environmental impact of livestock production and how plant-based diets can help protect the planet.
"Minimalism": a film that explores how less stuff can mean more happiness and a smaller ecological footprint.
"Our Planet": a Netflix documentary series that shows the beauty of nature and highlights its threats.
Useful websites
www.zerowasteeurope.eu: A European platform dedicated to the zero waste lifestyle, offering guides, articles and inspiration
www.greenpeace.org: An environmental organisation that provides up-to-date information on environmental campaigns and opportunities to get involved.
www.vegansociety.com: A site dedicated to veganism that offers recipes, tips and information about the impact of a plant-based diet on the planet.
Organic apps and tools
Ecosia: A search engine that uses ad profits to plant trees.
JouleBug: An app that motivates you to adopt sustainable habits through challenges and games.
My Footprint: a tool to calculate your ecological footprint and tips on how to reduce it.
Too Good To Go: An app that helps reduce food waste by offering unsold food at reduced prices.
These resources can help you better understand sustainability issues and find concrete steps you can take. Whether you choose to deepen your knowledge, track your progress, or get involved in green initiatives, every step counts. Get started today and get inspired by these useful tools!





